DENTAL RESTORATION / FILLING
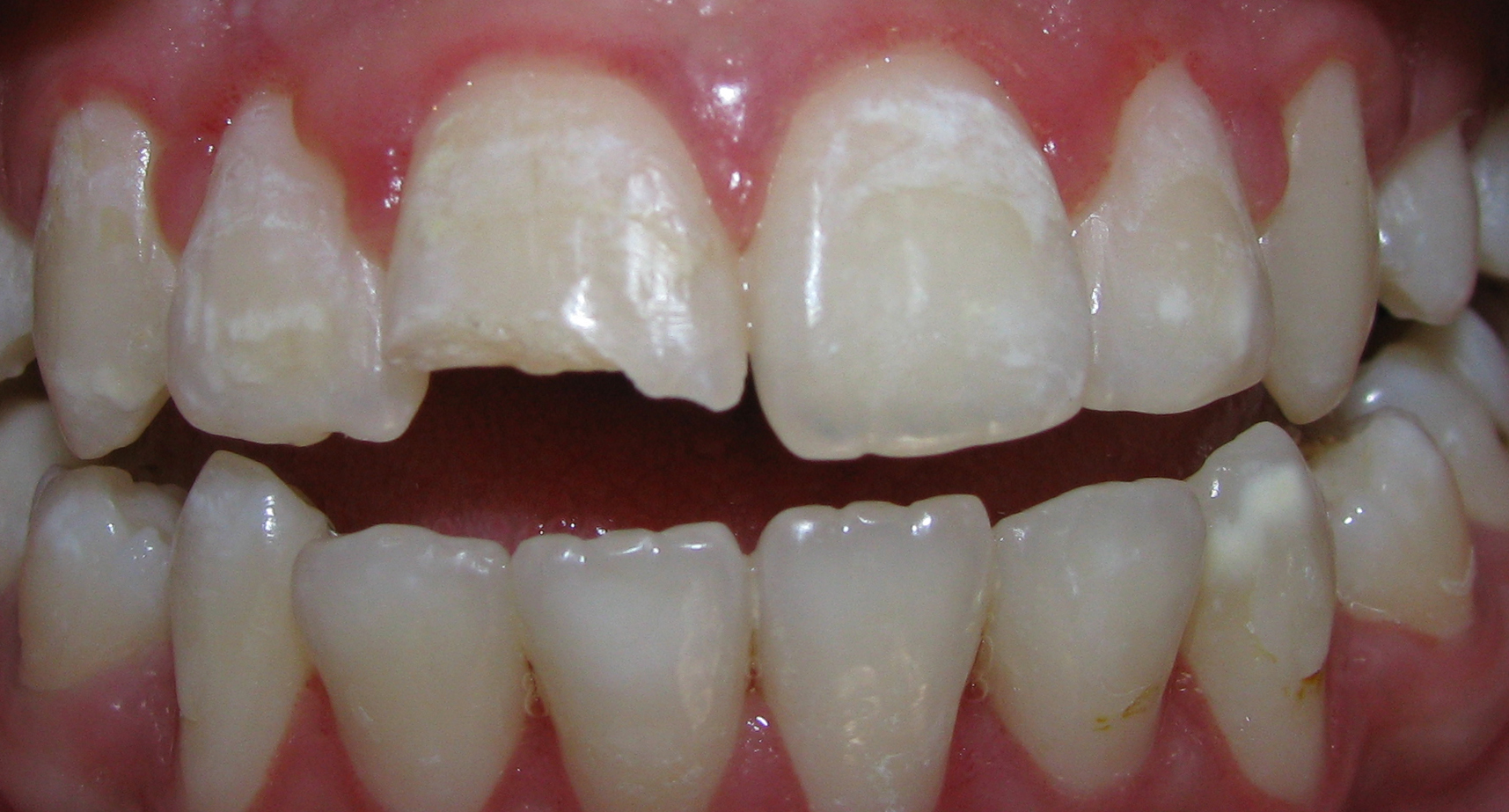
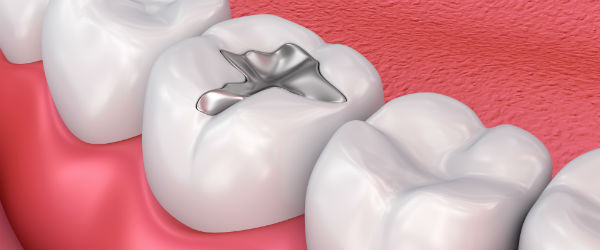
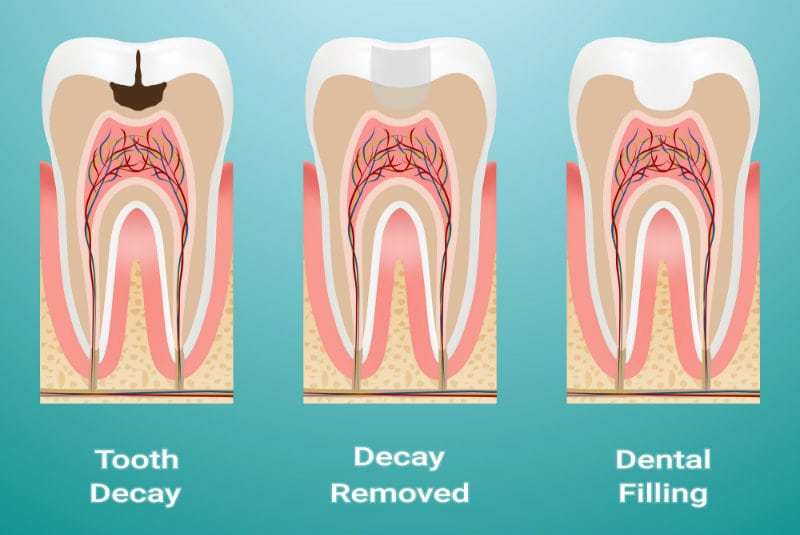
Dental restorations or Fillings are used to replace the parts of the tooth that have been lost, due to a number of reasons. These include wear and tear, decay and accidental damage. There are a variety of different materials that can be used for filling teeth. The most common type of filling is the Composite Filling. Composite or white fillings are less obvious (as compared to Silver Amalgam fillings) and more natural looking. They are almost identical to the natural tooth.
Direct Restoration
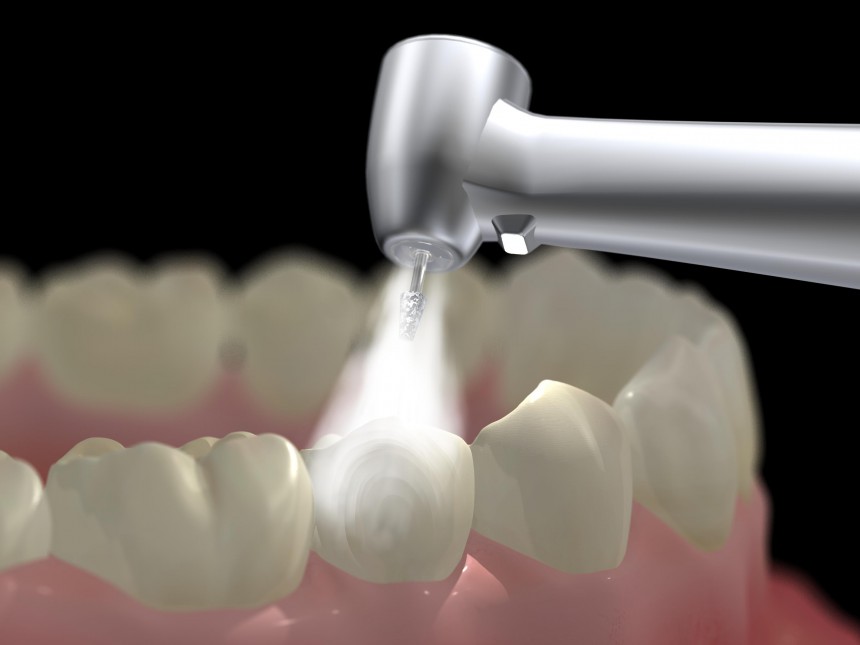
The materials of choice today are Composites Resins because they are tooth coloured & mimic the natural appearance of tooth structure. As the name indicates, a composite material, either a plastic or resin is bonded to an existing tooth. Achieving a flawless surface, repairing the look of the tooth and strengthening it in the process. As with all restorations, composite bonds require proper care and regular cleaning. In order to ensure they last as long as possible, composites should be brushed and flossed daily. Often used to improve the appearance of your teeth and enhance your smile.
Composite Bonding Is A Common Solution For
- Fixing or repairing chipped or cracked teeth
- Reducing unsightly gaps or spaces between teeth
- Hiding discoloration or faded areas on the tooth’s surface
Composite Bonding Has Many Advantages
It is a quick process which typically lasts less than one hour.
It does not reduce the tooth’s original structure and is relatively inexpensive.
Composite resins come in many different shades and provide better matching of shades to the natural colour of your teeth.
Other materials used are Glass Ionomer Cements, nowadays which are reinforced with resins to increase strength and aesthetics (translucency).
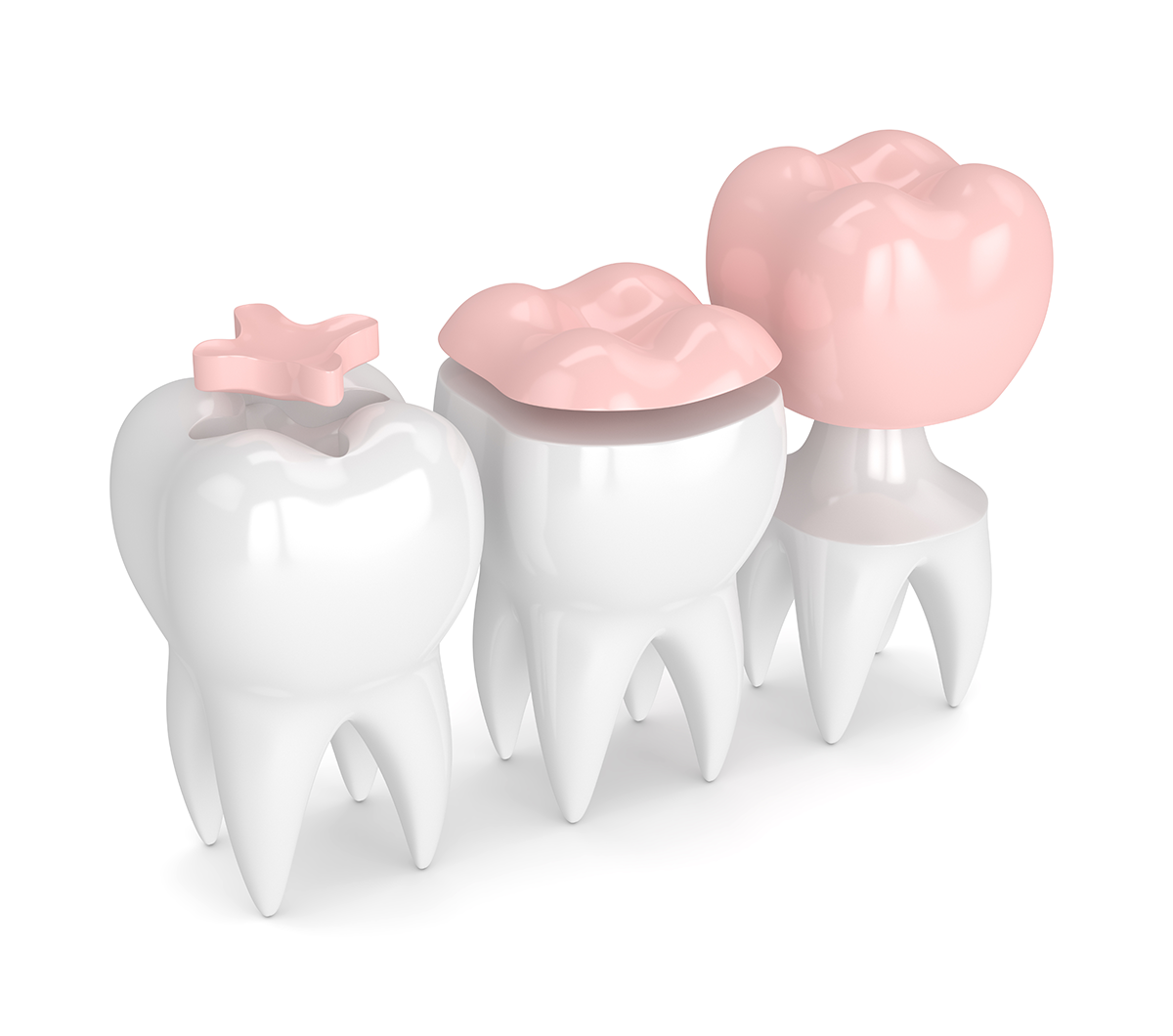
Indirect Restoration
Sometimes a tooth is planned to be restored with an intracoronal restoration, but the decay or fracture is so extensive that a direct restoration would compromise the structural integrity of the restored tooth or provide improper occlusal or biting forces. In such situations, indirect restorations like Inlays and Onlays may be fabricated. An only is the same as an inlay, except that it extends to replacing a cusp.
Inlays and Onlays are done in two dental visits. Usually a dental technician fabricates the indirect restoration from records that we provide of the prepared tooth. The finished restoration is bonded permanently with resin cement. Common indirect restorations are done using composites, ceramics, or zirconia.